
Surrogate mother is in possession of an eligibility certificate issued by appropriate authority
Following are the conditions:
A certificate of medical & psychological fitness from RMP
Surrogacy is a method where a woman (surrogate) carries a baby for intended parents who may be unable to conceive or carry a pregnancy. The surrogate agrees to undergo pregnancy and childbirth on behalf of the intended parents. It offers hope to couples facing infertility issues. If you’re considering surrogacy, at Ankoor fertility clinic, a reputable surrogacy centre in Mumbai can provide guidance and support throughout the process.

The intended parent(s) are person or persons who become the legal parent(s) of a child born through surrogacy.
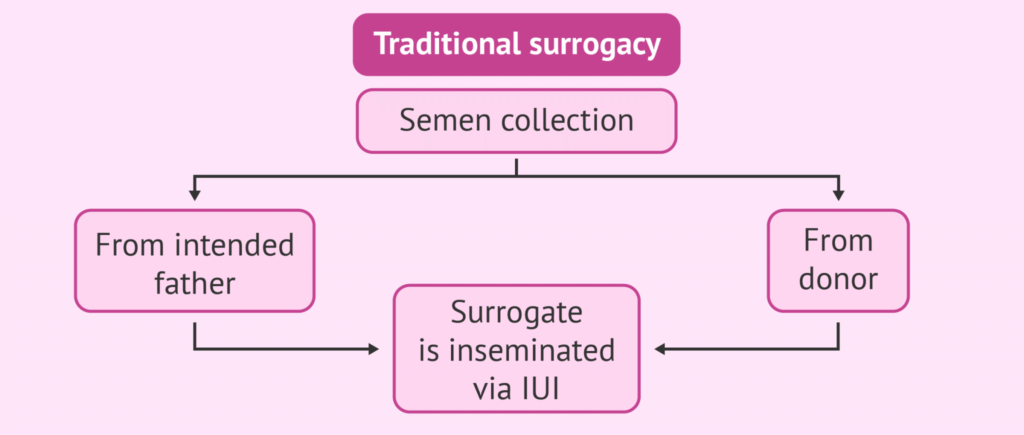
1. Traditional Surrogacy: This is a pregnancy where a surrogate mother is artificially inseminated, either by the intended father or an anonymous donor and carries the baby to term. The child is thereby genetically related to both the surrogate mother, who provides the egg and the intended father or anonymous donor. This type of surrogacy is PROHIBITTED according to Indian government guidelines.
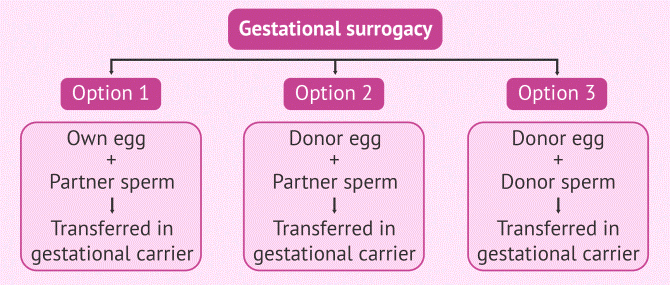
2. Gestational Surrogacy: This is a pregnancy where, IVF is used, either with the eggs of the intended mother, or donor and sperms of intended father or donor. The surrogate mother therefore does not use her own eggs, and is genetically unrelated to the baby
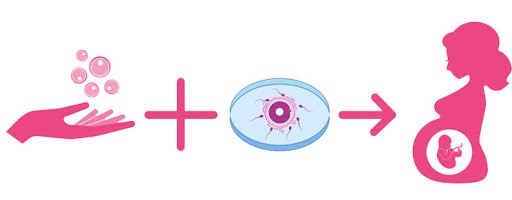
The female intended parent, or an egg donor, undergo special procedures to extract a number of eggs.
The eggs are fertilised with sperms of intended father or donor in the laboratory, resulting in embryos.
The embryo is transferred into the womb of the surrogate mother. The embryos can be transferred into the surrogate either ‘fresh’ or after having been thawed from the stock (frozen embryo transfer- FET). For a fresh embryo transfer the cycles of the surrogate and the egg donor must be synchronised, and this is done using hormone medications and injections. In cases, where embryos have been frozen already and the thawed embryos are being transferred, the surrogate mother is provided with hormone medications for preparing her endometrial lining, in a planned cycle.
A couple who will raise the child once it is handed over to them by the surrogate is known as a commissioning couple or intended parent. The commissioning couple may both be the genetic parents, or just one or neither of them may be genetically related to the child.
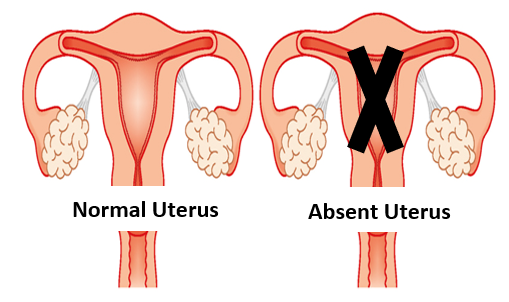
Below are a few listed medical conditions wherein it may be difficult or sometimes impossible to bear a child in your own womb:
The success rate of surrogacy in Mumbai, like here at Ankoor Fertility Clinic is very good with an implantation rate of around 80% and a carry home baby rate of around 60%.
An eligibility certificate for intending couple is issued separately by appropriate authority.
Surrogate mother is in possession of an eligibility certificate issued by appropriate authority
Prohibition of conducting surrogacy
Written informed consent of surrogate mother
Prohibition to abandon child born through surrogacy
It is very much possible that the intending parent can feed her baby in spite of not carrying her in her womb.
The different ways of breastfeeding-
Just because the baby is born through surrogacy does not mean he or she cannot receive breast milk and the many health benefits it provides.
The commissioning/intending mother can give her own breast milk to the baby, in spite of not carrying the baby in her womb. This can be done by ‘induced lactation’.
Induced lactation has been embraced by the nursing community as a welcome method to enhance the bonding relationship between a new mother and baby born through surrogacy. We at Ankoor Fertility Clinic, a leading surrogacy centre in Mumbai, start preparing the intending mother for this induced lactation from the 6th month of gestation itself. This has given us very good results.

A women who carries the child in her womb, for couple who are unable to conceive due to specific reasons is a surrogate mother. As a surrogate, you have the chance to make parenthood possible for someone who otherwise would not have the opportunity.
Surrogates are selected only in the early reproductive years (up to 35 years) of her life and she should have already proven her fertility by giving birth to her own child.
The surrogate and her partner are screened for the following. A detailed history of the surrogate and her husband is taken.
We at Ankoor Fertility Clinic, also carry out blood tests and screen for any hormonal abnormality in the surrogate, any major blood disorder, and infections that can be transmitted to the baby. Detailed pelvic sonography is done to ensure maximum chances of success. We also do blood tests of the surrogate’s husband to screen for any infectious diseases that may be transmitted to the baby.
What is Gestational surrogacy?
Indications for surrogacy
Different combinations of IVF with surrogacy
What is the surrogacy procedure ?
What is the surrogacy procedure?